Ripple XRP
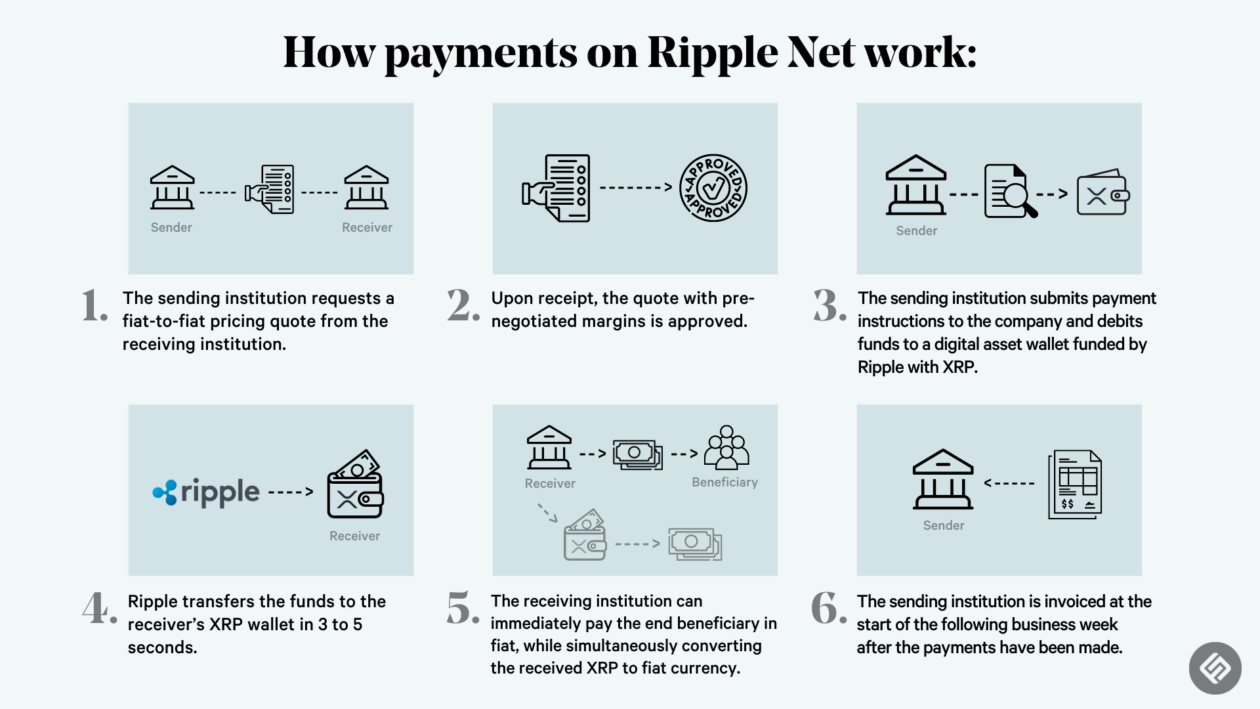


Ripple XRP is a cryptocurrency and payment network that aims to facilitate fast, efficient, and low-cost international payments. It has gained significant attention in the financial sector, attracting both investors and businesses seeking to streamline their cross-border transactions.
Origins and History
Ripple, the company behind XRP, was founded in 2011 by Jed McCaleb and Chris Larsen. The initial focus was on developing a peer-to-peer payment network called RipplePay, which later evolved into the current RippleNet platform. XRP, the native cryptocurrency of the Ripple network, was introduced in 2012 as a bridge currency for facilitating cross-border transactions.
XRP Technology
XRP operates on a decentralized, open-source ledger known as the XRP Ledger. This ledger is maintained by a network of validators, ensuring the security and integrity of transactions. XRP uses a unique consensus mechanism called “XRP Consensus Ledger” (XCL), which differs from the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus used by Bitcoin. XCL relies on a distributed network of validators to reach consensus on the validity of transactions, making it faster and more energy-efficient than PoW.
Key Features and Advantages
- Speed and Efficiency: XRP transactions are typically processed within seconds, significantly faster than traditional bank transfers.
- Low Transaction Fees: XRP transactions are associated with minimal fees, making it a cost-effective option for cross-border payments.
- Scalability: The XRP Ledger is designed to handle a high volume of transactions, making it suitable for large-scale financial operations.
- Global Reach: XRP can be used to facilitate payments in any currency, making it a truly global payment solution.
Comparison with Other Cryptocurrencies and Payment Systems
Ripple XRP distinguishes itself from other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum in its focus on facilitating cross-border payments. While Bitcoin and Ethereum primarily serve as decentralized digital currencies, XRP is designed to streamline financial transactions between institutions. Compared to traditional payment systems like SWIFT, Ripple XRP offers faster transaction speeds, lower fees, and greater transparency.
Potential Use Cases and Applications
- Cross-Border Payments: XRP can facilitate fast and cost-effective international money transfers, benefiting businesses and individuals.
- Remittances: XRP can be used to send money to family and friends abroad at lower costs than traditional remittance services.
- Micropayments: XRP’s low transaction fees make it suitable for small-value payments, such as online content subscriptions or digital goods purchases.
- Trade Finance: XRP can be used to settle trade transactions more efficiently and transparently, reducing delays and costs.
Ripple XRP



Ripple XRP, a cryptocurrency designed for cross-border payments, has been a subject of significant scrutiny and legal battles due to its unique design and its relationship with the Ripple Labs company. Understanding the regulatory landscape surrounding Ripple and XRP is crucial for comprehending its future prospects and the challenges it faces.
Regulatory Landscape and Legal Battles
The regulatory landscape surrounding Ripple and XRP has been characterized by uncertainty and evolving interpretations of existing laws. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States has been particularly active in scrutinizing Ripple, claiming that XRP is an unregistered security. The SEC filed a lawsuit against Ripple Labs in December 2020, alleging that the company raised billions of dollars through unregistered securities offerings. This lawsuit has been a significant hurdle for Ripple and has created uncertainty for XRP holders and investors.
The SEC’s case against Ripple is based on the Howey Test, a legal framework used to determine whether an asset is a security. The Howey Test considers four factors:
- An investment of money
- In a common enterprise
- With the expectation of profits
- Solely from the efforts of others
The SEC argues that Ripple Labs’ sales of XRP meet all four criteria, making it a security. However, Ripple Labs maintains that XRP is a digital currency and not a security, emphasizing its decentralized nature and use as a medium of exchange.
The legal battle between Ripple and the SEC has been ongoing, with both sides presenting their arguments and evidence. The outcome of this case could have significant implications for the broader cryptocurrency industry, as it could set a precedent for how other digital assets are classified.
Impact of Regulations on Ripple and XRP
The outcome of the SEC’s case against Ripple could have a significant impact on the future of the company and XRP.
If the SEC wins, XRP could be classified as a security, requiring Ripple Labs to register it with the SEC. This could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny, potentially limiting XRP’s growth and adoption.
However, if Ripple Labs prevails, XRP could be recognized as a digital currency, potentially boosting its adoption and value.
Regardless of the outcome, the legal battle has already had a significant impact on Ripple and XRP. The uncertainty surrounding the regulatory landscape has made it challenging for Ripple Labs to secure partnerships and expand its business.
Challenges in Navigating the Regulatory Environment
Ripple and XRP face several challenges in navigating the regulatory environment:
- Uncertainty and Evolving Regulations: The cryptocurrency industry is constantly evolving, and regulatory frameworks are still being developed. This creates uncertainty for companies like Ripple, making it difficult to plan for the future and comply with changing regulations.
- Varying Regulatory Approaches: Different countries have different regulatory approaches to cryptocurrencies. This creates challenges for companies like Ripple, which operate globally. Ripple needs to navigate complex and often conflicting regulatory frameworks.
- Lack of Clarity on Classification: There is a lack of clarity on how digital assets like XRP should be classified. The SEC’s case against Ripple highlights this ambiguity. This uncertainty can deter investors and hinder adoption.
Addressing the Challenges, Ripple xrp
Ripple has taken several steps to address the challenges it faces in the regulatory environment:
- Engaging with Regulators: Ripple has been actively engaging with regulators worldwide, providing information and seeking clarity on regulatory expectations. This proactive approach can help build trust and foster a more collaborative relationship with regulators.
- Building Partnerships: Ripple has been building partnerships with financial institutions and governments to promote the adoption of XRP and its payment solutions. These partnerships can help demonstrate the value of XRP and gain support for its use.
- Investing in Technology: Ripple has been investing in technology to improve its payment solutions and make them more compliant with regulatory requirements. This investment can help Ripple stay ahead of the curve and demonstrate its commitment to responsible innovation.
Ripple XRP



Ripple XRP is a cryptocurrency that operates on the Ripple network, a decentralized platform designed for fast and efficient cross-border payments. While XRP is often associated with Ripple, it’s important to understand that the two are distinct entities. Ripple, the company, develops and maintains the Ripple network, while XRP is the native cryptocurrency used for transactions on this network.
Market Dynamics and Adoption
The market capitalization and trading volume of XRP are significant indicators of its popularity and potential. XRP’s market capitalization, which reflects the total value of all XRP in circulation, has fluctuated significantly over the years, mirroring the broader cryptocurrency market trends. However, it consistently ranks among the top ten cryptocurrencies by market capitalization. Trading volume, which measures the amount of XRP exchanged on various cryptocurrency exchanges, also plays a crucial role in determining the price of XRP. Higher trading volume generally indicates greater interest and liquidity in the cryptocurrency.
The adoption of XRP by financial institutions and businesses is a key driver of its value and price. Ripple has focused on partnering with banks and financial institutions to facilitate cross-border payments using its network and XRP. These partnerships aim to streamline international transactions, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. As more financial institutions adopt XRP and the Ripple network, the demand for XRP is likely to increase, potentially leading to higher prices.
Several factors influence the price and value of XRP, including:
* Supply and Demand: The supply of XRP is fixed at 100 billion, with a significant portion held by Ripple. The demand for XRP is driven by its use in transactions on the Ripple network, as well as speculation and investment.
* Adoption by Financial Institutions: As more financial institutions adopt the Ripple network and use XRP for transactions, the demand for XRP is likely to increase.
* Regulatory Environment: Regulatory clarity and acceptance of cryptocurrencies, including XRP, are crucial for its wider adoption and price stability.
* Market Sentiment: The overall sentiment towards cryptocurrencies and the broader financial market can significantly impact the price of XRP.
Comparing the adoption rate of XRP with other cryptocurrencies is essential for understanding its relative position in the market. While Bitcoin and Ethereum remain the dominant cryptocurrencies in terms of market capitalization and adoption, XRP has carved a niche for itself in the cross-border payments space. The adoption rate of XRP is particularly noteworthy in the financial services sector, where its focus on efficiency and speed has attracted interest from banks and payment providers.
| Year | Price (USD) | Volume (USD) | Adoption Events |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | $0.25 – $3.84 | $1 billion – $10 billion | – Ripple partners with American Express to streamline cross-border payments. – Ripple launches xRapid, a solution for real-time cross-border payments using XRP. |
| 2018 | $0.30 – $3.40 | $2 billion – $15 billion | – Ripple partners with MoneyGram to facilitate cross-border payments using XRP. – Ripple announces partnerships with several banks and financial institutions globally. |
| 2019 | $0.25 – $0.45 | $1 billion – $5 billion | – Ripple continues to expand its network of partners, including banks in Asia and Europe. – The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) launches an investigation into Ripple’s XRP sales. |
| 2020 | $0.15 – $0.35 | $1 billion – $3 billion | – Ripple faces regulatory challenges and legal scrutiny from the SEC. – The COVID-19 pandemic impacts the global economy and cryptocurrency markets. |
| 2021 | $0.40 – $1.80 | $3 billion – $10 billion | – Ripple continues to develop its technology and expand its network of partners. – The SEC sues Ripple for allegedly selling unregistered securities. |
Ripple XRP, a cryptocurrency designed for facilitating cross-border payments, has gained traction in the financial sector. While its future remains uncertain, its potential impact on global finance is undeniable. The trajectory of XRP mirrors the rise of individuals like alex highsmith , who have defied expectations to achieve remarkable success.
Like XRP, Alex Highsmith’s journey is a testament to the power of innovation and perseverance in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Ripple XRP, a cryptocurrency designed for cross-border payments, has seen its value fluctuate significantly in recent years. While its future remains uncertain, the digital currency’s potential to revolutionize global finance is undeniable. The rapid rise of innovative technologies, such as those employed by rising NFL star alex highsmith , is a testament to the transformative power of disruption.
Similarly, XRP’s decentralized nature could disrupt traditional banking systems, offering faster and more cost-effective solutions for international transactions.
